Empowering Financial Solutions - Money on Chain | Rootstock (RSK)

Description
Money on Chain provides a Bitcoin-Collateralized Stablecoin. This solves the biggest problem for Bitcoin mainstream adoption: the volatility problem. The Dollar On Chain, a Bitcoin-Backed Stablecoin, uses a trust minimized, decentralized system.
Within the Money On Chain architecture, we distinguish the following Platform users (some users may have more than one role, that is, it may be a MoC holder and a stablecoin holder):
Stablecoin User: A user who does not want to be exposed to the volatility of a cryptocurrency, so he prefers to own a token that follows the price of a FIAT currency Bitcoin Holder: People who save their bitcoins for the long term and seek an income on their bitcoins.
Leveraged BTC Trader: A user looking to perform leveraged operations in BTC.
MoC Holder: A user who acquires MOC, which allows him to participate in the government of the platform and / or provide a service to it in exchange for receiving subsidies and part of the fees collected by the platform.
Any Rootstock Token (ART) Trader: A user who owns a token compatible with the Rootstock Blockchain (could be BPro, DoC, MoC, rBTC, RIF, etc), and wants to perform a decentralized exchange operation. Smart Contracts: gets data from OMoC
How Money on Chain integrates with Rootstock
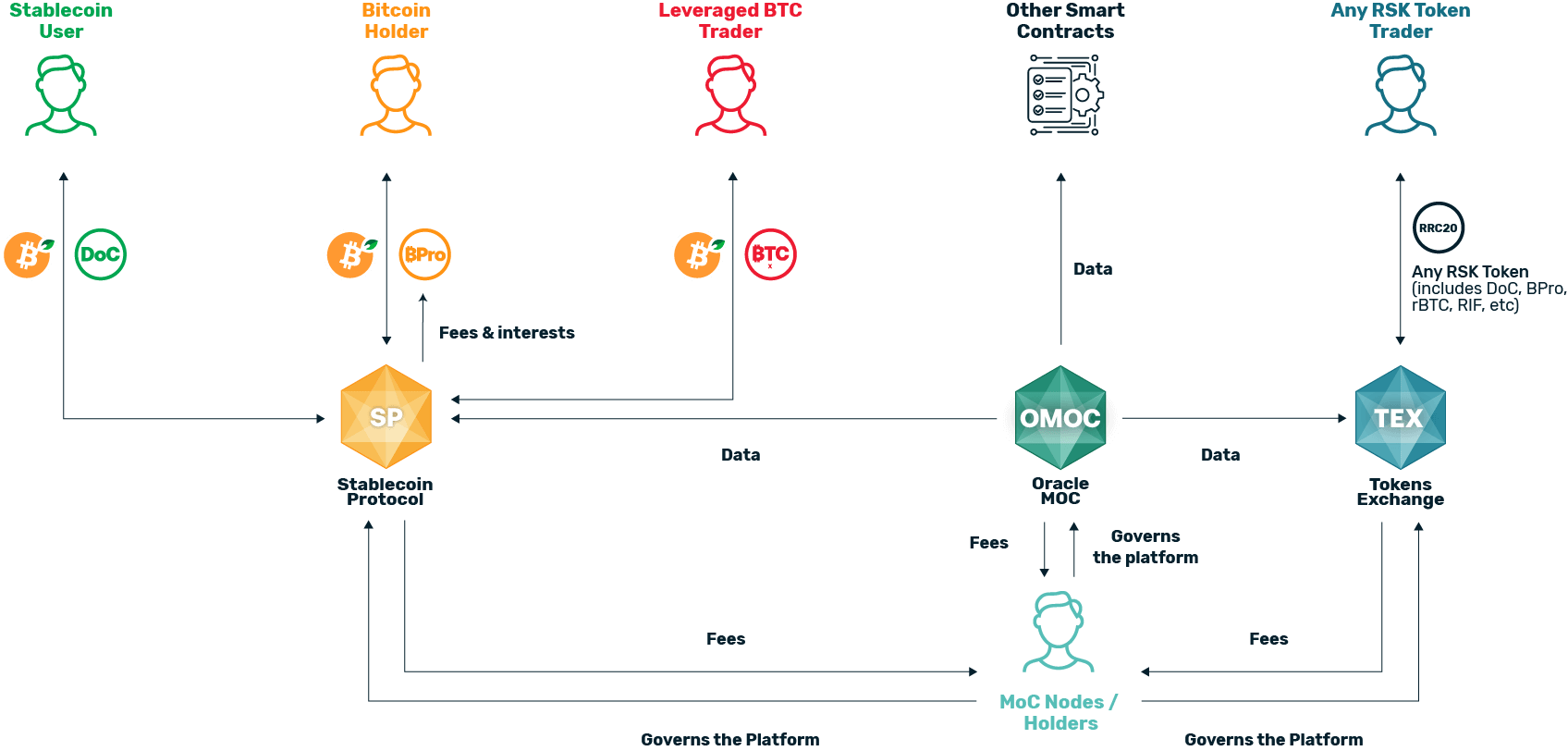
How Money On Chain Works
Money on Chain's Goal
The financial system is up against some serious challenges. Its overheads are large, transactions are slow, and frictions abound. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have emerged as alternatives to traditional fiat money, but they have proven to be extremely volatile. This limits their use. MOC's goal is to provide a Bitcoin-Collateralized Stablecoin, which solves the biggest problem for Bitcoin mainstream adoption: the volatility problem. The Dollar On Chain, a Bitcoin-Backed Stablecoin, uses a trust minimized, decentralized system.
Functionality
The Bitcoin-collateralized stablecoin uses a trustless, decentralized two-token system. The undesirable volatility of Bitcoin will be stripped into two separate currencies and a derivative financial instrument.
Components
- Dollar On Chain (DoC)
- BitPro (BPro)
- BTCX
- Money On Chain Token (MoC)
- Tokens Exchange (Tex)
- Oracles Money On Chain (OMoC)
A Bitcoin-collateralized stablecoin minimizes counterparty risk through a set of smart contracts. The stable token, DOC, is pegged to the Rootstock network’s native token, RBTC, which acts as collateral – though other collateral may be used to maintain pegs. RBTC is linked 1 : 1 to Bitcoin (1 RBTC = 1BTC) and is convertible to and from BTC. The Dollar on Chain (DOC), which is an RRC20 token, is pegged to the US dollar for risk-averse individuals, while the BitPro, also an RRC20 token, maintains Bitcoin’s price volatility. BTCX are positions in the system’s decentralized derivatives exchange (DEX). MOC Protocol, a set of smart contracts, returns the amount of DOCs equivalent to the amount of dollars received in RBTC at the time of confirmation of the transaction. BitPro is issued when RBTCs are sent to MOC Protocol. The system returns the equivalent amount at the time the transaction is recorded on the blockchain. The MoneyOnChain decentralized exchange’s native token, the non-transferable BTCX, represents leveraged positions on the price of RBTC, and they are created when an address sends RBTC to the smart contract. Participants purchase BitPros with RBTCs, and redeem them for RBTC at which time they are burned.
Description of the model behind MOC Protocol
MoC Protocol is a set of smart contracts developed in order to represent the model behind the DAO MoneyOnChain. The version 0.2 of the model is described here. However, several improvements have already been developed for this model that will be published in future versions of this document and will be implemented in future versions of MOC Protocol. For all the examples and descriptions it is assumed that the stable token is pegged to the US dollar and that the collateral used is RBTC, however, with the appropriate parameters, it is possible to use another collateral or maintain another peg, but in that case, the less inflationary asset should be used as collateral of the other.
The peg 1RBTC = 1BTC is considered valid.
Introduction
The model was designed to align the economic incentives of the different actors with the objective of maintaining the peg 1DOC = 1USD. It was not designed taking current stable coins implementations but it solves its liquidity known problems. It Identifies and aligns the interests of three types of cryptocurrency users.
- The Dollar on Chain (DOC), is a RRC20 token pegged to the US Dollar for risk-averse individuals. Those who need a stable currency use the DOC, a token that maintains a peg with the US dollar. There is more than 4B usd already in these types of assets.
- The BitPro, is a RRC20 token for Bitcoin holders seeking a passive income in RBTC. Bitcoin holders, people who save their bitcoins for the long term and seek an income on their bitcoins, use BitPro, which is a token that pays a bitcoin interest rate in addition to being slightly leveraged, which increases the holding of RBTC when the price goes up. The rate is variable, and depends on market conditions. 65% of all bitcoins are in possession of these types of holders.
- BTCX are positions in a decentralized derivatives exchange (DEX). Traders looking for leverage during the RBTC price rise can use the BTCX which are positions leveraged in the RBTC price, these positions work as a future that expires every 90 days. The annual volume of these types of instruments is over 1 Trillion.
- In Rootstock the SmartBitcoin (RBTC) is linked 1: 1 to Bitcoin (1 RBTC = 1BTC), and can be converted in a decentralized way to and from BTC.
Asset types
Fungible tokens
| Symbol | Name | Token Standard | Network |
|---|---|---|---|
| DOC | Dollar on Chain | ERC20 | Rootstock |
| BPRO | BitPro | ERC20 | Rootstock |
Non-token financial assets
| Symbol | Name | Network |
|---|---|---|
| BTCX | BTCX | Rootstock |
Documentation
Tutorials
- Getting Started with Money on Chain
- How to configure a Wallet to get BPRO
- Python API to Money On Chain projects
- Video Tutorials
User Guides
Reference Docs
API Docs
- RBTC-collateralized stablecoin contract
- Money on Chain API
- Money on Chain Oracle
- Money on Chain Price Feeder
- Money on Chain Governance Smart Contract System